|
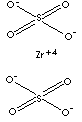
ZIRCONIUM SULFATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 14644-61-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 238-694-4 | |
| FORMULA | Zr(SO4)2 | |
| MOL WT. | 283.34 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | Zirconium (IV) sulfate; Sulfuric acid, zirconium(4+) salt (2:1); | |
| Zirconiumsulfat (Dutch); Sulfato de circonio (Spanish); Sulfate de zirconium (French); | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white powder | |
| MELTING POINT | 410 | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 3.22 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
| |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
| |
| AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| FLASH POINT | None flammable | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions | |
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ZIRCONIUM & ITS COMPOUNDS | ||
Zirconium is a metallic transition element in Group IVb of periodic table; symbol
Zr, hard,
malleable, ductile, lustrous, silvery gray; atomic number 40; atomic mass
91.224; melting point ca 1,852°C; boiling point ca 4,377°C; specific gravity
6.56 g/cm3; valence +2,+3 or +4; electronic config. [Kr]4d25s2. It is light but
Its hardness is similar to copper. It has a hexagonal close-packed crystalline
structure resembles titanium. It is insoluble in water, soluble in hot or
concentrated acids, flammable as powder. Zirconium is mainly (almost 90% among
whole zirconium production) used in nuclear reactors due to its property of low
absorption for thermal neutrons, in addition to its extremely resistance to heat
and corrosion. It is applied in tubes for cladding uranium oxide fuel. Zirconium
is a fairly abundant element and the chief ore is zircon (neosilicate mineral
occurring in tetragonal prisms, ZrSiO4, also known as hyacinth; jacinth;
zirconite) which contains Zirconium and hafnium at a ratio of about 50 : 1.
Hafnium which absorbs neutrons readily should be removed for the usage of
zirconium in nuclear reactors. The other ores are baddeleyite (the oxide),
monazite, ilmenite, and rutile. Zirconium is usually alloyed with other metals
to make corrosion-resistant alloys. The chief comsumption in chemical industry
field is for piping against corrosion, in ceramic, refractory compounds,
pyrotechnics, welding fluxes, and explosives. Zirconium compounds are also used in
TiO2 pigment coating and leather
tanning. Zirconium forms a number of
compounds as below:
|
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white powder | |
| ZrO2 (HfO2) |
33 - 34 % | |
|
SIO2 |
0.015% max | |
|
Fe2O3 |
0.005% max | |
|
Na2O |
0.02% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
25kg or 1,000kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| PRICE INFORMATION |
||